Filter Results
Model reveals new details about the relationship between seabirds and forage fish fisheries
Forage fish, like anchovies and sardines, are a dietary staple for seabirds. Around the globe, seabirds have adapted in order to cope with natural changes in the availability of these prey fish. However, increased fishing pressure on these forage species is thought to be altering this predator-prey relationship in an adverse way for seabird populations. The natural ability of seabirds to cope with changes in prey abundance makes it difficult for researchers to determine if they are responding to natural processes or to human fishing practices.
Read moreLast ice-covered parts of summertime Arctic Ocean vulnerable to climate change
The region north of Greenland and the Canadian Arctic has been termed the Last Ice Area, where sea ice will remain the longest in summertime, providing a refuge for ice-dependent Arctic species. But conditions last summer show that parts of this region are already experiencing less summer ice due to climate change.
Read moreSpecimens by the Millions: Managing Large, Specialized Collections at the University of Washington Burke Museum Fish Collection
A new paper by Katherine Pearson Maslenikov published in Ichthyology and Herpetology outlines the history of the UW Fish Collection and its long partnership with NOAA and other state and federal agencies.
Read moreAcoustics under the ice: a complete story of marine life temporal cycles
Silvana González, a PhD student at the University of Washington School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences, uses acoustic techniques to collect data in otherwise inaccessible locations. In high-latitude marine ecosystems, like the Chukchi Sea, traditional vessel-based sampling for fish and zooplankton is only possible in seasons without sea ice. This limiting factor results in an incomplete picture of the life history of these species and the ecosystem as a whole. By utilizing remote acoustic measurements recorded throughout the year and under the sea ice, González is able to piece together a more complete picture of arctic marine life.
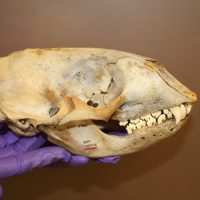
Read moreHarbor seal skulls provide clues to Puget Sound’s past food webs
The adage “you are what you eat” generally turns out to be true. Foods we ingest are broken down into amino acids and absorbed into our bodies, leaving trace elements in our bones. In turn, these amino acids can be traced back to their source like a biological receipt, revealing information about the environment. Using this knowledge, researchers are conducting isotope analysis of amino acids in harbor seal skulls to determine the composition of historical marine food webs.
Read more‘By-the-wind sailor’ jellies wash ashore in massive numbers after warmer winters
Thanks to 20 years of observations from thousands of citizen scientists, University of Washington researchers have discovered distinct patterns in the mass strandings of by-the-wind sailor jellies. Specifically, large strandings happened simultaneously from the northwest tip of Washington south to the Mendocino coast in California, and in years when winters were warmer than usual.
Read moreDNA sequencing reveals genetic basis of herring biodiversity
Herring that spawn at different times of the year are genetically distinct from one another, according to a new paper published Feb 24th in the Proceedings of the Royal Society B. The study, led by Eleni Petrou and Lorenz Hauser from the University of Washington School of Aquatic and Fishery Sciences, shows that populations of Pacific herring along the US west coast are genetically structured based on when they spawn and secondarily, where they spawn.
Read moreLogging change in Puget Sound: Researchers use UW vessel logbooks to reconstruct historical groundfish populations
To understand how Puget Sound has changed, we first must understand how it used to be. But unlike most major estuaries in the U.S., long-term monitoring of Puget Sound fish populations did not exist until 1990. Now researchers have discovered an unconventional method to help fill in gaps in the data: old vessel logbooks.
Read moreUsha Varanasi featured in Food for Thought: Luminaries Collection
Affiliate faculty Usha Varanasi recently published an article as part of the ICES Journal of Marine Science (ICES JMS) Food for Thought: Luminaries Collection, a curated collection of articles written by distinguished luminaries in the field of Marine Science.
Read moreIn Brazil, many smaller dams disrupt fish more than large hydropower projects
A new University of Washington paper quantifies the tradeoffs between hydroelectric generation capacity and the impacts on river connectivity for thousands of current and projected future dams across Brazil. The findings confirm that small hydropower plants are far more responsible for river fragmentation than their larger counterparts due to their prevalence and distribution.
Read more