Filter Results
Scientists Believe Evolution Could Save Coral Reefs, If We Let It
Coral reefs can adapt to climate change if given the chance to evolve, according to a study led by Coral Reef Alliance, Rutgers University, the University of Washington and other institutions.
The recent study, published in the journal Nature Ecology and Evolution, finds that coral reefs can evolve and adapt to the effects of climate change—but only if we protect a sufficient diversity of coral reefs, particularly when it comes to temperatures.
Newly documented population of polar bears in Southeast Greenland sheds light on the species’ future in a warming Arctic
A new population of polar bears documented on the southeast coast of Greenland use glacier ice to survive despite limited access to sea ice. This small, genetically distinct group of polar bears could be important to the future of the species in a warming world.
Read moreSound solutions for Seattle’s salmon
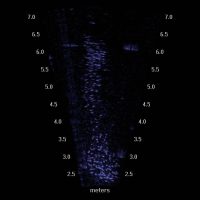
By mounting a specialized mobile sonar called a DIDSON (Dual-frequency IDentification SONar) under a kayak, UW research scientist Kerry Accola is able to count the juvenile salmon along the shoreline from the water’s surface. The sonar is capable of capturing high fidelity images during the day and also the night, when normal visibility is greatly reduced.
Read moreSAFS Research Roundup: Washington’s Sea Otters and Whale Twins
Graduate student Jessie Hale released a paper rethinking the status, trends, and equilibrium abundance estimates of Washington State’s sea otter population and Ruth Drinkwater’s (BS 2021) capstone project, “Estimating proportions of identical twins and twin survival rates in cetaceans using fetal data,” was published in Marine Mammal Science.
Read moreProtected tropical forest sees major bird declines over 40 years
SAFS Emeritus Professor Jim Karr began a long-term bird study in Panama 55 years ago while he was a Ph.D. student and later as a professor of ecology at the University of Illinois. He explains that the core of the current study design and its methodology were initiated in 1977. The study continues to this day under its third generation of leadership.
Read moreA decade of deep-reef exploration in the Greater Caribbean
A new paper co-authored by researchers at the Smithsonian’s Tropical Research Institute (STRI) and National Museum of Natural History (NMNH), the University of Washington and the Universidad Nacional Autónoma de Honduras describes the important contribution of submersibles to increasing our knowledge about the diversity of deep-reef fishes in the Greater Caribbean.
Read moreAnaerobic processes fuel carbon dioxide production in Tonle Sap Lake
Tropical rivers like the Mekong uniquely overflow their banks and flood for much of the year. These regular flood events create the chemical preconditions needed for methanogenesis to occur in waterlogged soils. A new study led by the University of Washington found that anaerobic processes occurring on floodplains of the Tonle Sap, the largest lake in Southeast Asia, are important contributors of the carbon dioxide that is dissolved in surface waters.
Read moreNew Center for Environmental Forensic Science aims to disrupt and dismantle international illegal wildlife trade
Across the globe, endangered species are at risk for illegal poaching. African elephants are sought out for their ivory, rhinoceros for their singular horns, and armadillo-like pangolins for their protective, brittle scales. Add to that list valuable and environmentally sensitive trees illegally harvested throughout the world where entire ecosystems are being deforested and illegal, unreported and unregulated fishing that is devastating oceans. These illicit markets, estimated at $1 trillion annually, cause enormous environmental impacts and have the potential to unleash new, deadly pathogens.
Read moreShifting ocean closures best way to protect animals from accidental catch
Many nations are calling for protection of 30% of the world’s oceans by 2030 from some or all types of exploitation, including fishing. Building off this proposal, a new analysis led by the University of Washington looks at how effective fishing closures are at reducing accidental catch. Researchers found that permanent marine protected areas are a relatively inefficient way to protect marine biodiversity that is accidentally caught in fisheries. Dynamic ocean management — changing the pattern of closures as accidental catch hotspots shift — is much more effective.
Read moreExploring the social and economic impacts of MSC certification
Professor Chris Anderson’s new research published in Frontiers in Marine Science explores the different social and economic impacts and pathways through which the MSC Certification Program can lead to sustainable outcomes for our oceans.
Read more